EN ISO 13849-1 is the main standard for the design of safety related control systems in the machinery safety department. The standard is now supplemented by FDAM (final revised draft of international standards) and fpra (final revised draft of European standards).
The main changes are as follows: with regard to the control system category used to determine the performance level PL, the potential and effective value of the PL of the mean time between dangerous failures (mttfd) of the class 4 system has been increased from the current 100 years to 2500 years. This means that more subsystems can be integrated into security functions than before. This is particularly beneficial to systems with multiple security functions. For hydraulic components, the mttfd value may reach 1200 years in the future, depending on the number of annual operations. Another new development involves category 2 systems, which previously envisaged a test frequency 100 times higher than the required safety functions. The test can now be carried out at or immediately before the safety function is required, provided that the reaction speed of the safety system is sufficient to protect the operator.
Added "overlapping hazards": in order to quantify the risks, each hazard can be considered individually, such as in the work area that does not overlap with the work area. Only when there are multiple risks in the same place at the same time, different risks need to be considered together. According to the current technical level, the core aspect of the future standard will include determining the overall failure probability of safety functions by summing up the PHF values of subsystems.
Other changes involve the description of parameters F and P when assigning risks to corresponding performance levels. "New" 13849-1 has been released as a unified version of ISO standard at the end of 2015, and will be introduced into the European standard as an en standard at the beginning of 2016.
The myocardial infarction grade (PL) system of EN ISO 13849-1 is based on quantification. It is said that the standard setter decided to use quantitative methods, which can compare megabytes with the safety integrity level (SIL) system for hazards, and provide a basis for the verification requirements of EN ISO 13849-2. According to this system, engineers can calculate the performance level of control related safety components (spr/cs) for each designated safety function. First, qualitative analysis is needed to determine the performance level (PLR) required for each safety function. EN ISO 13849-1 includes the following clauses:
4.3 determination of the required performance level (PLR) -- as mentioned in Clause 4.3 of EN ISO 13849-1, the performance level (PLR) of each safety function and is determined by using ground volume analysis.
4.3 determine the learned performance level (PLR) -- for each designated safety function performed by srp/cs, it is necessary to determine the required performance level (PLR) and file it.
Risk assessment can determine the required performance level, but it also determines the amount of risk that needs to be reduced in the safety related parts of the control system. The greater the risk of srp/cs reduction, the higher the value of PLR. In the figure below, three issues that need to be considered in the qualitative analysis process are described: the severity of injury, the frequency of exposure to danger, and the probability of avoiding danger. The new standard stipulates that the calculated PL must be greater than or equal to PLR.
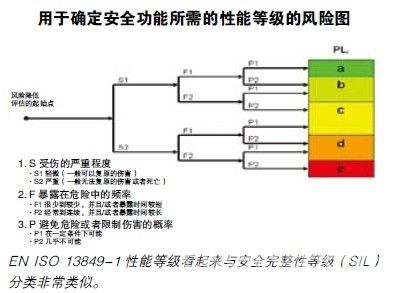
Category requirements defined in ISO 13849-1